Growers are continuously seeking alternative and safer ways to grow crops and plants that do not require large pieces of land. This has led to the invention of soilless production systems such as hydroponics and aquaponics that can be applied on large-scale commercial productions or small-scale home gardens.
Why Soilless Gardening?
Traditional gardening is the most common method used for growing plants as it provides adequate support, nutrition, air, and water required for the healthy growth of the plants. However, based on the principle that plants do not need soil to grow but use it for its nutrients only, a soilless growing method has become possible through the use of technology. Soilless agriculture refers to the growing of crops in a different growing media, substrates, or nutrient-rich solution instead of soil.
Soilless agriculture can be performed in a controlled environment and established anywhere as it is not dependent on land space and fertility. That is why it is considered the future method of farming in many parts of the world, and many people are turning to soilless methods of growing plants.
Benefits of Soilless Gardening
- Soilless growing methods have a low environmental impact because it is controlled agriculture.
- Low water usage in soilless gardening because of the closed-loop nature of growing.
- Crops grown in soilless gardening are of better quality than grown in traditional gardening.
- Soilless gardening has a lower concern of chemical, pesticide, and GMO produces.
- Ideal for urban gardening because it does not require a large space of land and can be installed indoors, on rooftops, or in the backyard.
- It offers year-round gardening if installed indoors or in a greenhouse.
- Higher yield because crops grown in soilless methods grow faster than in other gardening methods.
- No weeding, so it requires little maintenance.
- Satisfaction in knowing you feed your family with healthy food grown in your garden.
Soilless Gardening Systems
At present, there are three commonly used soilless production systems. These are hydroponics, aquaponics, and aeroponics. This article will focus on hydroponics and aquaponics because these two systems follow almost similar principles and are popular amongst home gardeners.
What is Hydroponics?
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without using soil by using mineral nutrient solutions, oxygen, and water. Plants in hydroponics are grown with their roots exposed to the nutritious water, or the roots may be supported by an inert medium such as expanded clay, gravel, or other substrates. When a plant’s root system is exposed directly to water and nutrition, it does not have to exert energy in finding nutrients to sustain its growth. The energy the roots might have used in acquiring food and water can be redirected into the plant’s growth, resulting in healthy and blooming fruits and flowers.
Plants sustain themselves by a process called photosynthesis. Plants do not need soil to photosynthesize. They only need the soil to supply them with the necessary water and nutrients. When nutrients are dissolved in the water, they can be applied directly to the root by flooding or immersion. The hydroponic methods have proven that direct exposure to nutrient-filled water can grow plants more effectively than traditional irrigation.
Pros of Hydroponics
- Hydroponics uses ten times less water than soil gardening.
- You can grow anywhere, as you don’t need fertile soil and large space to grow crops.
- You can have control over the nutrient balance.
- Less labor because there is no weeding involved.
- You can grow crops all year round.
- Plants grow faster in hydroponic systems than in soil-based gardening.
- Have a much higher crop yield than aquaponics.
Cons of Hydroponics
- Setting up a hydroponics system can be costly.
- Required more supervision than soil gardening.
- Power outages can affect hydroponic gardens.
- Waterborne diseases can spread quickly.
- Hydroponics nutrients can be expensive because of scarcity.
What is Aquaponics?
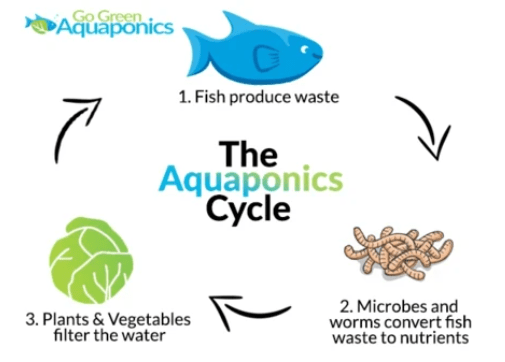
Aquaponics is a growing plant method that combines aquaculture (raising of fish and other aquatic animals) and hydroponics. A simple aquaponics system involves the growing of plants and raising fish with the help of beneficial bacteria. Plants, fish, and beneficial bacteria must work symbiotically to create a successful aquaponics system.
In aquaponics, plants are grown in the grow bed, and fish are raised in the fish tank. The water from the tank that contains fish waste is pumped to the grow bed, where the beneficial bacteria break the ammonia in the fish waste into nitrites and then nitrates. Plant roots absorb these nitrates to help them thrive, and in return, the roots clean and filter the water before it goes back into the fish tank, where the cycle will begin again.
Pros of Aquaponics
- Environmentally friendly because aquaponics does not use harmful chemicals because it can hurt the fish.
- Aquaponics uses up to 10 times less water than soil gardening.
- Climate adaptive because plants can be grown in greenhouses where temperature can be controlled.
- Fish waste is the main source of nutrients resulting in organic, chemical-free yields.
- Higher yields because fish and plants can be an additional source of income.
Cons of Aquaponics
- An aquaponics system can be costly to set up.
- It takes a few weeks before an aquaponics system is ready, as it requires cycling.
- An aquaponics system requires regular fish feeding and maintenance.
- An aquaponics system needs to stay well-balanced to run effectively.
- Balancing an aquaponics system can be tricky.
- Power outages may kill the fish, so the system needs a power backup.
- Mechanical failures are more common in aquaponics.
- It has a ratio of water to plants that limits the number of plants you can grow.
The Difference Between Hydroponics and Aquaponics
Raising fish to provide nutrients in aquaponics systems is the most apparent difference between hydroponics and aquaponics. However, there are still some significant differences between the two systems that are important to mention. These are:
| Hydroponics | Aquaponics | |
| Definition | Growing of plants without soil using a nutrient solution | Growing of plants and fish without soil using fish waste in a recirculating system. |
| Nutrient used | Chemical Nutrients | Fish produce fish waste that is converted into nitrates. |
| Costs | Less cost-effective because the chemical nutrients used are increasing because of scarcity. | Very cost-effective because organic matter is used to supply nutrients. |
| Startup Costs | Lower start-up cost. | Higher startup cost because of additional components like fish tanks, heater, etc. |
| Startup Speed | Fast to start up. | Slower to start up than hydroponics because new systems require cycling. |
| Temperatures | Aside from growing lights, the temperature is lower to prevent bacterial growth. | Require higher temperature to encourage bacterial growth |
| Productivity | Produce lower yields compared to aquaponics. | Higher yields than hydroponics because it can produce two sources of produce; fish and plants. |
| Maintenance | Requires a higher degree of maintenance as the water needs to be replaced regularly because of salt build-up, which is toxic to the plants. | The systems are easy to maintain. The water does not need replacement because it is a recirculating system. |
Similarities Between Hydroponics and Aquaponics
There are several similarities between hydroponics and aquaponics. These are:
- Both agricultural methods grow plants without the use of soil.
- Both systems use nutrient-rich water to grow plants.
- Each can produce higher yields than the traditional growing methods.
- Plants grown in hydroponics and aquaponics grow faster than other growing methods.
- Both can practice year-round gardening if built indoors or in a greenhouse.
- No weeding is involved in both systems, as there is no soil involved.
Which Method is the Best for You?
Hydroponics and aquaponics systems are closely tied together and follow many of the same principles, but delivery methods are very different. For home gardeners who want their own system but are having difficulty with what growing method to implement. Both approaches have their pros and cons; so much of the decision on what soilless gardening method to choose will depend on your needs, available space, startup cost budget, and the produce that you want to achieve from your home garden.
The Bottom Line on Hydroponics and Aquaponics
Whatever soilless gardening method you choose, you will have to invest time, money, and effort. However, the benefits you get from having your own garden at home that produces fresh, organic food for the family in an environmentally friendly way are worth all the time and money you spend building your own home garden.
- Strawberry Lemonade Recipe (no added sugar) - 03/20/2025
- Barndominiums: Weighing the pros and cons - 12/30/2024
- Ginger Orange Marmalade Recipe: Sweet, Tangy, and Just a Little Spicy - 11/09/2024